Chronic prostatitis is a slow prostate disease.For him, as for any other chronic pathology, changes in aggravation and reduction periods are characteristic.The disease develops slowly, with little anxiety to the patient early on, except for a single symptom that is usually not focused on.However, pathological progression can violate the development of prostate function and complications, so it is important to identify it at an early stage.
You can perform preventive tests on your urologist at the on-site clinic.If necessary, separate treatment options will be developed for you, thanks to you getting rid of the disease and avoiding complications in a short period of time.
Characteristics of the disease
Chronic prostatitis in men is one of the most common pathology of the genital system.About 30% of patients aged 20 to 50 years suffer.
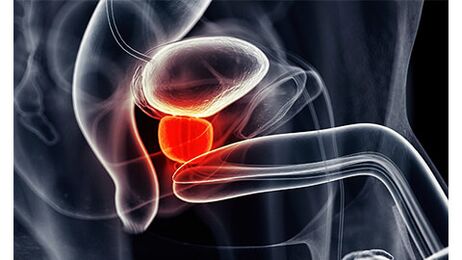
The prostate is a non-parallel organ located below the bladder.It is responsible for the quality of sperm: it produces a special secret and is an important part.During an erection, the prostate iron closes the outlet of the bladder.
Acute and chronic prostatitis are often the cause of infection (bacterial, viral, or fungal origin).Even if the focus of the infection is far from the prostate, they are able to penetrate the prostate through the blood (lymph).Similarly, infections usually fall directly from the urethra into the prostate.These two organs are interconnected: the prostate tube opens to the urethra.And it also passes through the initial part of the urethra through the prostate.
Infections can be listed in the prostate even without the presence of in vivo pathological processes.After all, each organ is characterized by its own microorganisms.Microorganisms living in the urethra are harmless in their "habitat".However, for the prostate, they may be aliens, and if they fall into it, they may cause the development of inflammation.
Prostatitis may be:
- Infectious - Caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
- Nature stagnates - develops with the stagnation of prostate secretion.
Causes of disease development
The cause of development depends on the form of chronic prostatitis.Infectious forms occur in the following diseases:
- Urethritis.
- Orchard (pneumonia in testicles).
- Cystitis.
The source of the infection does not have to be near the prostate.Pathology can occur in the context of other infections that progress in the body: dental caries, sinusitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, etc.
Similarly, chronic prostatitis can develop due to unequal bacterial origins.
Stagnation of prostate secretion occurs due to blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, which may be due to:
- Irregular sex life.
- Deposition.
- Wear tight underwear.
- Bad habits (alcoholic, smoking).
Stagnant forms were found in 85% of chronic prostatitis cases.
Factors that increase the risk of developing two forms of disease include:
- Conventional microorganisms, bruises in the pelvic organs.
- Improper nutrition.
- Neurological overload.
- A mistaken sex life.
- Hypothermia and staying in humid environments for a long time.
These factors either cause worsening blood supply to the pelvic organs or increase the likelihood of infection penetration into the prostate.
Diagnosis of chronic prostatitis is more frequently diagnosed with representatives of certain occupations than people with different activities.Risk groups include:
- Truck drivers and other drivers (forced to be in the same position for a long time).
- Programmer, office staff (sitting lifestyle).
- Fishermen (stayed in the cold for a long time).
- Professional athletes: football players, wrestlers, volleyball players, basketball players (usually risk of injury in the pelvic area).
- Sailors and geologists (face unfavorable weather conditions: cold, wet).
Chronic prostatitis: Symptoms

The symptoms of chronic prostatitis are:
- The pain of the bone, lower abdomen: it can be given to the rectum and ac bone.
- Erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, lack of ejaculation.
- Urination disorders: frequent urination impulses, difficulty in emptying the bladder, pain during urination.
In the early stages of chronic prostatitis, the symptoms are weaker.Pain is insignificant and past.Urination disorders occur irregularly.Therefore, patients usually do not bring these important symptoms to these symptoms and will not consult a doctor.He will attend the reception even if the signs of the disease are clearly expressed.
Even if there are rare symptoms, you can consult a doctor, otherwise the disease may lead to complications.
Complications of chronic prostatitis
The presence of a constant focus of infection can lead to its spread to other organs and pathological developments therein.The complications of chronic prostatitis are:
- Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder.
- Pyelonephritis - Pulsive nephritis
- veziculite - Inflammation of seed bubbles.
- Ladderitis - Inflammation of the testicles and their attachments.
Inflammatory diseases of the urogenital system can in turn lead to:
- Infertility.
- Prostate cancer disease.
- to prostate adenoma.
refer to!Erectile dysfunction occurs frequently in chronic prostatitis.This is due to the fact that the nerves that cause the erection pass through the prostate.This often affects them when one of the pathological processes develops.
diagnosis
To identify a disease, you need to visit a urologist or a hemologist.First, the doctor will collect anatomy: he will listen to the complaint and ask questions.He will then perform visual examinations on the prostate and finger examinations.Additionally, the following types of research may be required:
- Bacteriological examination of urine.
- Microscopic examination of prostate secretion.
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
- Sperm diagram.
- Urethral smear (to identify sexually transmitted infections).
- Prostate biopsy.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
The treatment of chronic prostatitis is mainly conservative.Surgery is performed only if treatment does not give the necessary results or complications:
- Abscess of the prostate or surrounding fabric.
- Prostate cancer.
- Prostate adenoma.
- Severe pathology of the urethra.
Conservative treatment involves appointments:
- Drugs: NSAIDs, antibiotics, alpha blockers, immunomodulators, drugs, accelerated regeneration.If you have severe pain, you can prescribe medicine.
- Prostate massage.Allows you to eliminate stagnation and improve blood circulation in affected areas and outflow of prostate secretion.However, other studies were conducted before prescribing massage because in some cases it can exacerbate this.
- Physical therapy procedure.The most common prescriptions are: magnetic therapy; electrophoresis; laser therapy; ultrasound therapy.
- diet.With its help, it happens: eliminating the risk of aggravated inflammation, improving the digestive tract, increasing immunity, reducing the load on internal organs, and normalizing blood circulation throughout the body.It is necessary to steam, cook or bake food in the oven with minimum salt.The basis of diet in chronic prostatitis is low-fat fish, lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, beef), cereals, vegetables, macaron products, made of whole wheat flour, light soup.It is necessary to exclude: fried, spicy, fat, smoked, salty food, canned food, semi-produced products, fast food, mushrooms, spices, including onions and garlic, citrus, legumes, legumes, fatty meat, fatty meat, strong tea, strong tea, alcohol, carbonate, carbonate beverages, candy, candy and concrete baking.
- In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed.Transurethral resection of the prostate - Removal of the pathological site or the entire prostate without cutting (introducing equipment through the urethra), usually open for the development of prostate adenoma.Prostatectomy - Follow the implementation of the section, remove the prostate or area thereof in the usual surgical manner.
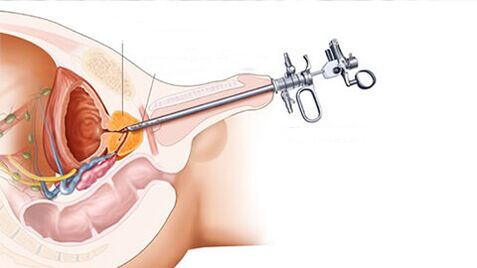
Prevent chronic prostatitis
In order to prevent the development of the disease, it is important to promptly eliminate any infection focus in the body.Regular sex life will benefit, excluding random relationships.A healthy and diverse diet and moderate physical exercise will boost immunity.It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, sit for a long time (if you need to work, you need to rest and choose), and stay close to your underwear.It is also important to prevent the annual examination of urologists.